Focusing
Focusing is the process defined as "Adapting information to the context of the end user for effective and optimal understanding of the information" without modifying the regulated content itself.
Core Principle
The fundamental constraint of Focusing is that regulated ePI content cannot be removed or altered. Focusing only changes:
- Visual representation (highlighting, collapsing)
- Supplementary content (adding hyperlinks, icons, videos)
- Organization and presentation
The Focusing Workflow
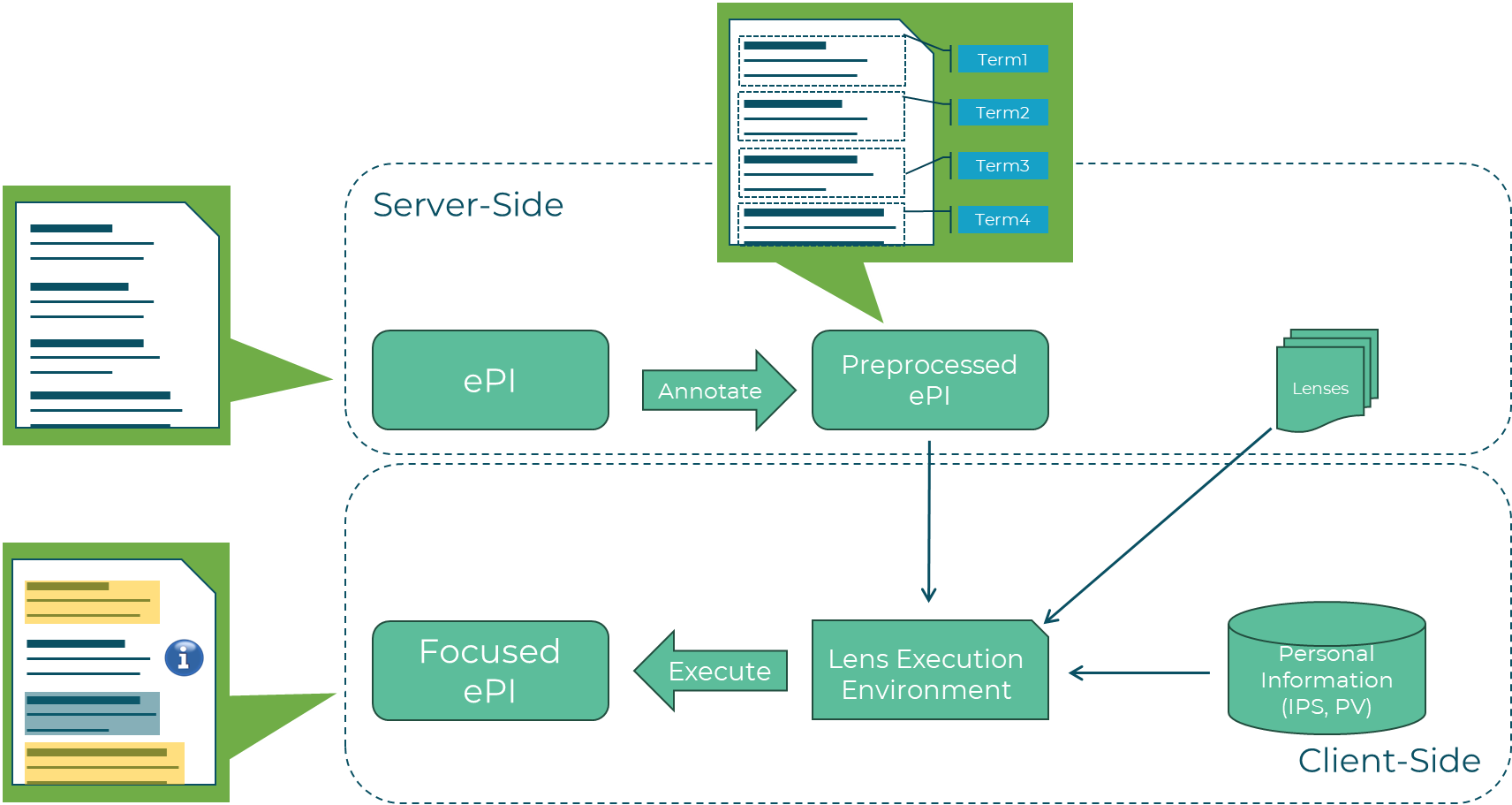
- Input: Raw ePI provided from Connectors
- Preprocessing: Preprocessors execute sequentially to create p(ePI) by adding semantic annotations using standard terminologies (e.g., SNOMED-CT).
- Lens Selection: Focusing Manager selects/discovers Lenses in server-side focusing
- Execution: LEE runs lens logic with IPS/PV
- Output: Focused ePI (f(ePI)) personalized for patient
Personalization Inputs
Focusing uses three critical inputs:
- p(ePI): Semantically annotated ePI
- IPS: Patient clinical data
- (Optional) PV: User context and preferences
Adaptation Techniques
Attention Detail Modification
- Highlight: Mark highly relevant sections (CSS class
"highlight") - Collapse: Minimize irrelevant sections (CSS class
"collapse") - Standard: Leave default presentation
See Attention Detail Modification for details.
Supplementary Content
- Add hyperlinks to Supporting Material
- Embed images, videos, pictograms
- Create interactive elements (glossary, hover boxes)
Execution modes
There are two main modes of executing the focusing process:
- Server-side focusing: Focusing Manager orchestrates the entire process and returns f(ePI) to client, meaning the server has access to IPS/PV data and can execute complex lenses with full context.
- Client-side focusing: Client retrieves p(ePI), lenses and executes lenses locally (e.g., embedding the LEE in a mobile app) for enhanced privacy and responsiveness.
Because the Focusing Manager is designed to be flexible, it supports explicit data input which defines a special case of client-side focusing where the client provides all necessary data (ePI, IPS, PV) in the request, allowing the server to execute lenses without needing to retrieve additional data from the FHIR Server. This mode is referred as hybrid-side focusing.
Result Characteristics
The f(ePI) is:
- Ephemeral: Not cached (always regenerated), in the same way as the IPS is ephemeral
- Personalized: Specific to one patient context
- Regulatory-compliant: Original content preserved
- Enhanced: With visual and supplementary adaptations
Related Concepts
- Focusing Manager - Orchestration component
- Preprocessor - Semantic annotation
- Lens - Adaptation logic
- LEE - Execution environment
- p(ePI) - Preprocessed input
- f(ePI) - Focused output
- G-lens - Overall solution